
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithm that use numerical approximation (as opposed to general symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics).
One of the earliest mathematical writings is a Babylonian tablet from the Yale Babylonian Collection (YBC 7289), which gives a sexagesimal numerical approximation of 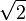 , the length of the diagonal in a unit square. Being able to compute the sides of a triangle is extremely important, for instance, in astronomy, carpentry and construction.
, the length of the diagonal in a unit square. Being able to compute the sides of a triangle is extremely important, for instance, in astronomy, carpentry and construction.
Numerical analysis continues this long tradition of practical mathematical calculations. Much like the Babylonian approximation of 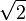 , modern numerical analysis does not seek exact answers, because exact answers are often impossible to obtain in practice. Instead, much of numerical analysis is concerned with obtaining approximate solutions while maintaining reasonable bounds on errors.
, modern numerical analysis does not seek exact answers, because exact answers are often impossible to obtain in practice. Instead, much of numerical analysis is concerned with obtaining approximate solutions while maintaining reasonable bounds on errors.
Undergraduate
